Computer Science Sample Paper 2
Computer Science questions and answers with explanation for interview, competitive examination and entrance test. It's contains are more AGRE test in computer science as well as GATE, PSC, NET and other similar exams.
1. . The line graph L(G) of a simple graph G is defined as follows:
• There is exactly one vertex v(e) in L(G) for each edge e in G.
• For any two edges e and e' in G, L(G) has an edge between v(e) and v(e'), if and only if e and e' are incident with the same vertex in G.
Which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
(P) The line graph of a cycle is a cycle.
(Q) The line graph of a clique is a clique.
(R) The line graph of a planar graph is planar.
(S) The line graph of a tree is a tree.
-
(A) P only (B) P and R only
-
(C) R only (D) P, Q and S only
Answer: A
2. What is the logical translation of the following statement ?
"None of my friends are perfect."
-
(A) ∃x(F(x)˄¬P(x)) (B) ∃x(¬F(x)˄P(x))
-
(C) ∃x(¬F(x)˄¬P(x)) (D) ¬∃x(F(x)˄P(x))
Answer: D
3. Consider the following sequence of micro–operations.
MBR←PC
MAR←X
PC←Y
Memory←MBR
Which one of the following is a possible operation performed by this sequence ?
-
(A) Instruction fetch
-
(B) Operand fetch
-
(C) Conditional branch
-
(D) Initiation of interrupt service
Answer: D
4. Consider a hard disk with 16 recording surfaces (0−15) having 16384 cylinders (0−16383) and each cylinder contains 64 sectors (0−63). Data storage capacity in each sector is 512 bytes. Data are organized cylinder–wise and the addressing format is <cylinder no., surface no., sector no.>. A file of size 42797 KB is stored in the disk and the starting disk location of the file is <1200, 9, 40>. What is the cylinder number of the last sector of the file, if it is stored in a contiguous manner?
-
(A) 1281
-
(B) 1282
-
(C) 1283
-
(D) 1284
Answer: D
5. The number of elements that can be sorted in Θ(logn) time using heap sort is
-
(A) Θ(1) (B) Θ(√logn)
-
(C) Θ(logn/loglogn) (D) Θ(logn)
Answer: C
6. Consider the following function:
int unknown int n {
int i, j, k=0;
for(i=n/2; i≤n; i++)
for(j=2; j≤n; j=j*2)
k=k+n/2;
return (k);
}
The return value of the function is
-
(A) Θ(n2)
-
(B) Θ(n2logn)
-
(C) Θ(n3)
-
(D) Θ(n3logn)
Answer: B
7. Consider the following languages.
L1={0p1q0r|p,q,r≥0}
L2={0p1q0r|p,q,r≥0,p≠r}
Which one of the following statements is FALSE?
-
(A) L2 is context–free
-
(B) L1∩L2 is context–free
-
(C) Complement of L2 is recursive
-
(D) Complement of L1 is context–free but not regular
Answer: D
8. Consider the DFA A given below.
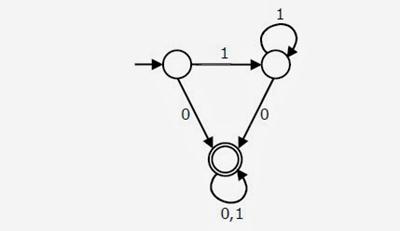
Which of the following are FALSE?
1. Complement of L(A) is context–free
2. L(A)=L((11*0+0)(0+1)*0*1*)
3. For the language accepted by A, A is the minimal DFA.
4. A accepts all strings over {0, 1} of length at least 2.
-
(A) 1 and 3 only (B) 2 and 4 only
-
(C) 2 and 3 only (D) 3 and 4 only
Answer: D
9. A shared variable x, initialized to zero, is operated on by four concurrent processes W, X, Y, Z as follows. Each of the processes W and X reads x from memory, increments by one, stores it to memory, and then terminates. Each of the processes Y and Z reads x from memory, decrements by two, stores it to memory, and then terminates. Each process before reading x invokes the Poperation (i.e., wait) on a counting semaphore S and invokes the V operation (i.e., signal) on the semaphore S after storing x to memory. Semaphore S is initialized to two. What is the maximum possible value of x after all processes complete execution?
-
(A) –2
-
(B) –1
-
(C) 1
-
(D) 2
Answer: D
10. Consider the following relational schema.
Students(rollno: integer, sname: string)
Courses(courseno: integer, cname: string)
Registration(rollno: integer, courseno: integer, percent: real)
Which of the following queries are equivalent to this query in English?
"Find the distinct names of all students who score more than 90% in the course numbered 107"
(I) SELECT DISTINCT S.sname
FROM Students as S, Registration as R
WHERE R.rollno=S.rollno AND R.Courseno=107 AND R.percent>90
(II) ∏sname(σcourseno=107∧percent>90(Registration⋈Students))
(III) {T|∃S ϵ Students, ∃R ϵ Registration(S.rollno=R.rollno∧
R.courseno=107∧R.percent>90∧T.sname=S.name)}
(IV) {<SN>|∃SR∃RP(<SR,SN>ϵStudents∧<SR,107,RP>ϵRegistration∧RP>90)}
-
(A) I, II, III and IV
-
(B) I, II and III only
-
(C) I, II and IV only
-
(D) II, III and IV only
Answer: A
11. Determine the maximum length of cable (in km) for transmitting data at a rate of 500 Mbps in an Ethernet LAN with frames of size 10,000 bits. Assume the signal speed in the cable to be 2,00,000 km/s
-
(A) 1
-
(B) 2
-
(C) 2.5
-
(D) 5
Answer: B
12. In an IPv4 datagram, the M bit is 0, the value of HLEN is 10, the value of total length is 400 and the fragment offset value is 300. The position of the datagram, the sequence numbers of the first and the last bytes of the payload, respectively are
-
(A) Last fragment, 2400 and 2789
-
(B) First fragment, 2400 and 2759
-
(C) Last fragment, 2400 and 2759
-
(D) Middle fragment, 300 and 689
Answer: C
13. The following figure represents access graphs of two modules M1 and M2. The filled circles represent methods and the unfilled circles represent attributes. If method m is moved to module M2 keeping the attributes where they are, what can we say about the average cohesion and coupling between modules in the system of two modules?
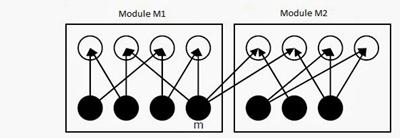
-
(A) There is no change.
-
(B) Average cohesion goes up but coupling is reduced
-
(C) Average cohesion goes down and coupling also reduces
-
(D) Average cohesion and coupling increase
Answer: A
14. A certain computation generates two arrays a and b such that a[i]=f(i) for 0≤i
Process X; Process Y;
private i; private i;
for (i=0; i<n; i++) { for (i=0; i<n; i++) {
a[i]=f(i); EntryY(R, S);
ExitX(R, S); b[i]=g(a[i]);
} }
Which one of the following represents the CORRECT implementations of ExitX and EntryY ?
(A) ExitX R, S {
P(R);
V(S);
}
EntryY R, S {
P(S);
V(R);
}
(B) ExitX R, S {
V(R);
V(S);
}
EntryY R, S {
P(R);
P(S);
}
(C) ExitX R, S {
P(S);
V(R);
}
EntryY R, S {
V(S);
P(R);
}
(D) ExitX R, S {
V(R);
P(S);
}
EntryY R, S {
V(S);
P(R);
}
Answer: C
15. Consider the following two sets of LR(1) items of an LR(1) grammar
X→c.X, c/d X→c.X, $
X→.cX, c/d X→.cX, $
X→.d, c/d X→.d, $
Which of the following statements related to merging of the two sets in the corresponding LALRparser is/are FALSE?
1. Cannot be merged since look aheads are different
2. Can be merged but will result in S–R conflict
3. Can be merged but will result in R–R conflict
4. Cannot be merged since goto on c will lead to two different sets
-
(A) 1 only (B) 2 only
-
(C) 1 and 4 only (D) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Answer: D
16. Which of the following is/are undecidable?
1. G is a CFG. Is L(G)=Φ?
2. G is a CFG. IS L(G)=∑* ?
3. M is a Turning machine. Is L(M) regular?
4. A is a DFA and N is a NFA. Is L(A)=L(N) ?
-
(A) 3 only
-
(B) 3 and 4 only
-
(C) 1, 2 and 3 only
-
(D) 2 and 3 only
Answer: D
17. What is the return value of f(p,p) if the value of p is initialized to 5 before the call? Note that the first parameter is passed by reference, whereas the second parameter is passed by value.
int f (int &x, int c) {
c=c-1;
if (c==0) return 1;
x=x+1;
return f(x,c)*x;
}
(A) 3024 (B) 6561
(C) 55440 (D) 161051
Answer: Marks to All
18. The preorder traversal sequence of a binary search tree is 30, 20, 10, 15, 25, 23, 39, 35, 42. Which one of the following is the postorder traversal sequence of the same tree?
-
(A) 10,20,15,23,25,35,42,39,30
-
(B) 15,10,25,23,20,42,35,39,30
-
(C) 15,20,10,23,25,42,35,39,30
-
(D) 15,10,23,25,20,35,42,39,30
Answer: D
19. Consider the following operation along with Enqueue and Dequeue operations on queues, where kis a global parameter.
MultiDequeue(Q) {
m=k
while(Q is not empty) and (m>0) {
Dequeue(Q)
m=m-1
}
}
What is the worst case time complexity of a sequence of n queue operations on an initially empty queue?
-
(A) Θ(n) (B) Θ(n+k)
-
(C) Θ(nk) (D) Θ(n2)
Answer: A
20. Consider an instruction pipeline with five stages without any branch prediction: Fetch Instruction (FI), Decode Instruction (DI), Fetch Operand (FO), Execute Instruction (EI) and Write Operand (WO). The stage delays for FI, DI, FO,EI and WO are 5 ns, 7 ns, 10 ns, 8 ns and 6 ns, respectively. There are intermediate storage buffers after each stage and the delay of each buffer is 1 ns. A program consisting of 12 instructions I1, I2, I3,….I12 is executed in this pipelined processor. Instruction I4 is the only branch instruction and its branch target is I9. If the branch is taken during the execution of this program, the time (in ns)needed to complete the program is
-
(A) 132
-
(B) 165
-
(C) 176
-
(D) 328
Answer: B
21. A RAM chip has a capacity of 1024 words of 8 bits each (1K×8). The number of 2×4 decoders with enable line needed to construct a 16K×16 RAM from 1K×8 RAM is
Answer: B
22. Which one of the following is NOT logically equivalent to ¬∃x(y()˄z())?
-
(A) x(∃z(¬)→y())
-
(B) x(z()→∃y(¬))
-
(C) x(y()→∃z(¬))
-
(D) x(∃y(¬)→∃z(¬))
Answer: Marks to All



