Computer Science Sample Paper 1
Computer Science questions and answers with explanation for interview, competitive examination and entrance test. It's contains are more AGRE test in computer science as well as GATE, PSC, NET and other similar exams.
1. A binary operation on a set of integers is defined as xy=x2+y2. Which one of the following statements is TRUE about ?
- (A) Commutative but not associative
- (B) Both commutative and associative
- (C) Associative but not commutative
- (D) Neither commutative nor associative
Answer: A
2. Suppose p is number of cars per minute passing through a certain road junction between 5 PM and 6PM, and p has a Poisson distribution with mean 3. What is the probability of observing fewer than 3 cars during any given minute in this interval?
- (A) 8/(2e3) (B) 9/(2e3)
- (C) 17/(2e3) (D) 26/(2e3)
Answer: C
3. Which one of the following does NOT equal
Answer: A
4. The smallest integer than can be represented by an 8-bit number in 2's complement form is
- (A) -256 (B) -128
- (C) -127 (D) 0
Answer: B
5. In the following truth table, V=1 if and only if the input is valid.
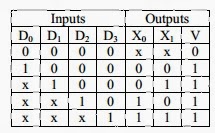
What function does the truth table represent?
- (A) Priority encoder (B) Decoder
- (C) Multiplexer (D) Demultiplexer
Answer: A
6. Which one of the following is the tightest upper bound that represents the number of swaps required to sort n numbers using selection sort ?
- (A) O(log n) (B) O(n)
- (C) O(n log n) (D) O(n2)
Answer: B
7. Which one of the following is the tightest upper bound that represents the time complexity of inserting an object into a binary search tree of n nodes ?
- (A) O(1) (B) O(log n)
- (C) O(n) (D) O(n log n)
Answer: C
8. Consider the languages L1 = Φ and L2 = {a}. Which one of the following represents L1L2*UL1* ?
- (A) { є } (B) Φ
- (C) a* (D) { є, a}
Answer: A
9. What is the maximum number of reduce moves that can be taken by a bottom-up parser for a grammar with no epsilon and unit-production (i.e., of type A→є and A→a) to parse a string with n tokens?
- (A) n/2 (B) n-1
- (C) 2n-1 (D) 2n
Answer: B
10. A scheduling algorithm assigns priority proportional to the waiting time of a process. Every process starts with priority zero(the lowest priority). The scheduler re-evaluates the process priorities every T time units and decides the next process to schedule. Which one of the following is TRUE if the processes have no I/O operations and all arrive at time zero?
- (A) This algorithm is equivalent to the first-come-first-serve algorithm.
- (B) This algorithm is equivalent to the round-robin algorithm.
- (C) This algorithm is equivalent to the shortest-job-first algorithm.
- (D) This algorithm is equivalent to the shortest-remaining-time-first algorithm.
Answer: B
11. Match the problem domains in Group I with the solution technologies in Group II.
Group I Group II
- (P) Services oriented computing (1) Interoperability
- (Q) Heterogeneous communicatingsystems (2) BPMN
- (R) Information representation (3) Publish-find bind
- (S) Process description (4) XML
- (A) P–1, Q–2, R–3, S–4
- (B) P–3, Q–4, R–2, S–1
- (C) P–3, Q–1, R–4, S–2
- (D) P–4, Q–3, R–2, S–1
Answer: C
12. The transport layer protocols used for real time multimedia, file transfer, DNS and email, respectively are
- (A) TCP, UDP, UDP and TCP
- (B) UDP, TCP, TCP and UDP
- (C) UDP, TCP, UDP and TCP
- (D) TCP, UDP, TCP and UDP
Answer: C
13. Using public key cryptography, X adds a digital signature σ to message M, encrypts <M,σ>, and sends it to Y, where it is decrypted. Which one of the following sequences of keys is used for the operations ?
- (A) Encryption: X’s private key followed by Y’s private key; Decryption: X’s public key followed by Y’s public key
- (B) Encryption: X’s private key followed by Y’s public key; Decryption: X’s public key followed by Y’s private key
- (C) Encryption: X’s public key followed by Y’s private key; Decryption: Y’s public key followed by X’s private key
- (D) Encryption: X’s private key followed by Y’s public key; Decryption: Y’s private key followed by X’s public key
Answer: D
14. Assume that source S and destination D are connected through two intermediate routers labelled R. Determine how many times each packet has to visit the network layer and the data link layer during a transmission from S to D.
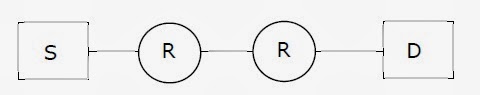
- (A) Network layer–4 times and Data link layer-4 times
- (B) Network layer–4 times and Data link layer-3 times
- (C) Network layer–4 times and Data link layer-6 times
- (D) Network layer–2 times and Data link layer-6 times
Answer: C
15. An index is clustered, if
- (A) it is on a set of fields that form a candidate key.
- (B) it is on a set of fields that include the primary key.
- (C) the data records of the file are organized in the same order as the data entries of the index.
- (D) the data records of the file are organized not in the same order as the data entries of the index.
Answer: C
16. Three concurrent processes X, Y, and Z execute three different code segments that access and update certain shared variables. Process X executes the P operation (i.e., wait) on semaphores a,b and c; process Y executes the P operation on semaphores b, c and d; process Z executes the Poperation on semaphores c, d, and a before entering the respective code segments. After completing the execution of its code segment, each process invokes the V operation (i.e., signal) on its three semaphores. All semaphores are binary semaphores initialized to one. Which one of the following represents a deadlock-free order of invoking the P operations by the processes?
- (A) X:P(a)P(b)P(c) Y:P(b)P(c)P(d) Z:P(c)P(d)P(a)
- (B) X:P(b)P(a)P(c) Y:P(b)P(c)P(d) Z:P(a)P(c)P(d)
- (C) X:P(b)P(a)P(c) Y:P(c)P(b)P(d) Z:P(a)P(c)P(d)
- (D) X:P(a)P(b)P(c) Y:P(c)P(b)P(d) Z:P(c)P(d)P(a)
Answer: B
17. Which of the following statements is/are FALSE?
- (1) For every non-deterministic Turing machine, there exists an equivalent deterministic Turing machine.
- (2) Turing recognizable languages are closed under union and complementation.
- (3) Turing decidable languages are closed under intersection and complementation
- (4) Turing recognizable languages are closed under union and intersection.
- (A) 1 and 4 only (B) 1 and 3 only
- (C) 2 only (D) 3 only
Answer: C
18. Which of the following statements are TRUE?
(1) The problem of determining whether there exists a cycle in an undirected graph is in P.
(2) The problem of determining whether there exists a cycle in an undirected graph is in NP.
(3) If a problem A is NP-Complete, there exists a non-deterministic polynomial time algorithm to solve A.
- (A) 1, 2 and 3 (B) 1 and 2 only
- (C) 2 and 3 only (D) 1 and 3 only
Answer: A
19. What is the time complexity of Bellman-Ford single-source shortest path algorithm on a complete graph of n vertices ?
- (A) Θ(n2) (B) Θ(n2logn)
- (C) Θ(n3) (D) Θ(n3logn)
Answer: C
20. In a k-way set associative cache, the cache is divided into v sets, each of which consists of k lines. The lines of a set are placed in sequence one after another. The lines in set s are sequenced before the lines in set (s+1). The main memory blocks are numbered 0 onwards. The main memory block numbered j must be mapped to any one of the cache lines from
- (A) (j mod v)*k to (j mod v)*k+(k−1)
- (B) (j mod v) to (j mod v)+(k−1)
- (C) (j mod k) to (j mod k)+(v−1)
- (D) (j mod k)*v to (j mod k)*v+(v−1)
Answer: A
21. Which one of the following expressions does NOT represent exclusive NOR of x and y?
- (A) xy + x'y' (B) x⊕y'
- (C) x'⊕y (D) x'⊕y'
Answer: D
22. Which one of the following functions is continuous at x = 3 ?
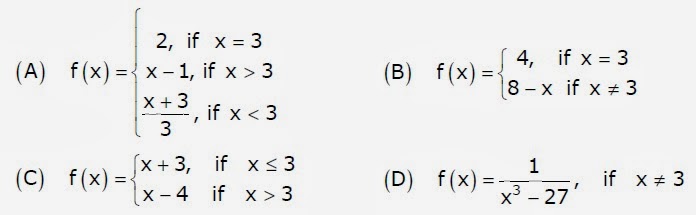
Answer: A
23. Function f is known at the following points:

The value of 0∫3f(x)dx computed using the trapezoidal rule is
(A) 8.983 (B) 9.003 (C) 9.017 (D) 9.045
Answer: D
24. Consider an undirected random graph of eight vertices. The probability that there is an edge between a pair of vertices is ½. What is the expected number of unordered cycles of length three ?
- (A) 1/8 (B) 1
- (C) 7 (D) 8
Answer: C
25. Which of the following statements is/are TRUE for undirected graphs?
P: Number of odd degree vertices is even.
Q: Sum of degrees of all vertices is even.
- (A) P only (B) Q only
- (C) Both P and Q (D) Neither P nor Q
Answer: C


